In a world where climate change feels like that annoying relative who just won’t leave, renewable energy technology shines like a superhero in spandex. It’s not just about saving the planet; it’s about embracing innovation that can power homes, businesses, and even your neighbor’s questionable karaoke nights—all without the guilt of fossil fuels.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview Of Renewable Energy Technology
Renewable energy technology encompasses various innovations designed to harness energy from natural sources. Solar power systems convert sunlight into electricity, providing a sustainable alternative to conventional energy methods. Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy from wind, generating power without emitting greenhouse gases. Hydropower plants utilize flowing or falling water to produce energy, demonstrating efficiency and reliability across many regions.
Biomass energy, derived from organic materials, plays a significant role in this sector. This technology transforms waste into usable energy, contributing to a circular economy. Geothermal systems tap into the Earth’s internal heat, offering consistent energy supply, especially in geologically active areas.
The adoption of renewable energy technology contributes to reduced dependence on fossil fuels. This transition facilitates a decrease in carbon emissions, promoting cleaner air and healthier environments. Many countries have established ambitious targets for increasing their renewable energy share, reflecting a collective effort toward sustainability.
Investment in these technologies often leads to job creation within local economies. Installing solar panels, constructing wind farms, and developing geothermal plants generate employment opportunities and stimulate economic growth. Additionally, innovation in energy storage systems enhances the efficiency of these technologies.
Collaboration among governments, businesses, and research institutions drives advancements in renewable energy. This partnership encourages the development of more efficient technologies and strengthens infrastructure. Achieving energy independence and security hinges on successfully implementing renewable energy solutions globally.
Types Of Renewable Energy Technologies
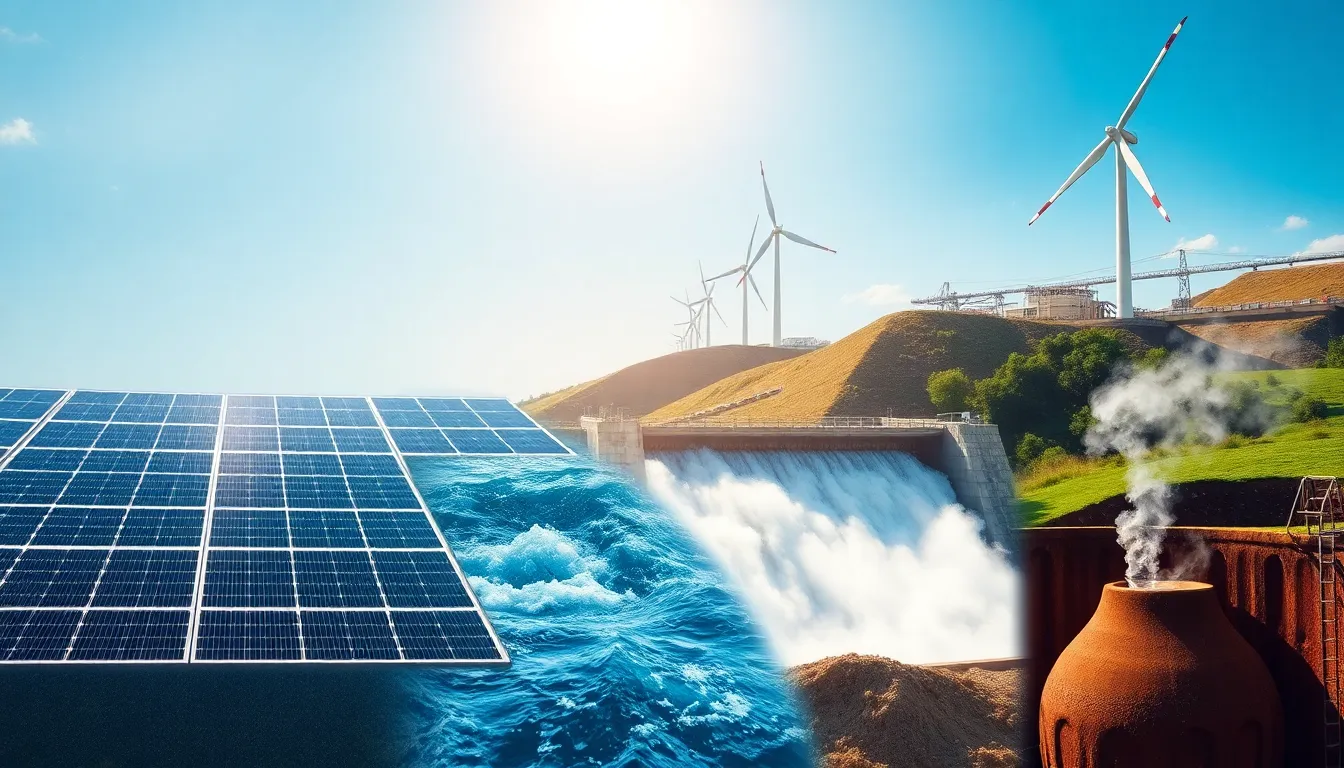

Renewable energy technologies harness natural resources to produce clean power. They significantly contribute to environmental sustainability and energy independence.
Solar Energy Technology
Solar energy technology converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. These cells, integrated into solar panels, offer a sustainable energy source for homeowners and businesses. Innovations in solar technology, such as solar thermal and concentrated solar power systems, enhance efficiency. The decreasing costs of solar installations have made it more accessible for widespread adoption.
Wind Energy Technology
Wind energy technology captures kinetic energy from wind using turbines. These turbines generate electricity by transforming wind motion into mechanical power. Offshore and onshore wind farms provide a significant portion of renewable energy globally. Continuous advancements in turbine design improve energy efficiency and reduce costs, promoting expanded use.
Hydropower Technology
Hydropower technology exploits flowing water to generate electricity. Dams and run-of-the-river systems capture water’s energy. This reliable source accounts for a substantial percentage of global renewable electricity generation. Innovative techniques, such as small-scale hydropower projects, enhance local energy solutions while minimizing ecological impact.
Biomass Energy Technology
Biomass energy technology produces energy from organic materials like plant waste and animal byproducts. This method converts biomass into biofuels or generates electricity through combustion processes. The versatility of biomass makes it a powerful renewable energy source, capable of utilizing various feedstocks. Its development supports waste reduction and contributes to local economies.
Geothermal Energy Technology
Geothermal energy technology harnesses heat from beneath the Earth’s surface for heating and electricity. This stable energy source features steam-driven turbines that generate power. Enhanced geothermal systems and binary cycle power plants expand geothermal’s range of applicability. The low emissions and constant availability position geothermal energy as a viable alternative in the renewable energy landscape.
Benefits Of Renewable Energy Technology
Renewable energy technology offers numerous advantages, providing significant benefits that extend beyond just energy production.
Environmental Impact
Reducing carbon emissions stands as one of the primary environmental benefits of renewable energy technology. Solar and wind energy systems significantly decrease harmful pollutants. Cleaner air contributes to improved public health, reducing respiratory problems linked to fossil fuels. Utilizing natural resources minimizes the ecological footprint, helping preserve biodiversity. Investment in renewables supports the transition to a sustainable energy landscape.
Economic Advantages
Job creation represents a key economic advantage of renewable energy technology. The renewable sector generated approximately 3.1 million jobs globally in 2020, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Local economies see stimulation through infrastructure projects and service demands. Lower operational costs associated with renewable technologies enhance long-term economic stability. Transitioning to renewables spurs innovation, driving advancements in related industries.
Energy Security
Achieving energy independence is crucial for national security. Renewable energy sources reduce reliance on imported fuels, providing stability in energy supply. Wind and solar farms can be strategically located, minimizing vulnerability to geopolitical tensions. Investing in renewable technology ensures a diversified energy portfolio, safeguarding against price volatility. Energy efficiency and innovation in this sector enhance long-term resilience, promoting self-sufficiency.
Challenges And Limitations
Renewable energy technology faces several significant challenges and limitations that can affect its broader adoption. Addressing these issues is crucial for maximizing its potential.
Technological Barriers
Technological barriers impede the widespread deployment of renewable energy solutions. System efficiency can vary significantly across different technologies, leading to concerns about energy reliability. Storage capabilities remain a critical issue, as many renewable sources rely on conditions that are not consistent, such as sunlight and wind. Innovations in battery technology are ongoing but still need improvement to enhance energy storage solutions. Intelligent grid systems must also advance to manage the integration of various energy sources effectively. Consequently, these barriers impact overall performance and growth in renewable energy markets.
Economic Constraints
Economic constraints play a vital role in limiting the expansion of renewable energy technology. Initial capital costs for renewable infrastructure often remain high, deterring potential investors. Financing options may be less accessible for smaller enterprises or communities. Market fluctuations can affect project viability, particularly when compared to the established fossil fuel industry. Many traditional energy sources enjoy longstanding subsidies that make it difficult for renewables to compete competitively in pricing. Investment in research and development is critical for driving down costs and enhancing economic viability.
Policy and Regulatory Issues
Policy and regulatory issues create hurdles that can hinder the progress of renewable energy technology. Government incentives and support vary widely across regions, leading to inconsistencies in investment levels. In some cases, outdated policies fail to recognize the advantages of renewable sources, favoring fossil fuels instead. Administrative processes often become lengthy and complicated, delaying project implementation. Effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders can improve the regulatory landscape. Streamlining regulations could enhance the adoption of renewable technologies across various sectors.
Future Trends In Renewable Energy Technology
Emerging technologies continue to shape the future of renewable energy. Innovations promise to enhance efficiency and sustainability across various sectors.
Innovations and Advancements
Solar panels are becoming more efficient, with recent advancements increasing conversion rates to over 25%. Wind turbine designs are evolving as manufacturers develop larger blades to capture more wind energy. Energy storage solutions, such as lithium-ion batteries, have improved, allowing for increased storage capacity and longevity. Additionally, breakthroughs in floating solar farms make solar power accessible in reservoirs and oceans. These innovations enhance deployment capabilities and enable cleaner energy generation on a larger scale.
Market Growth Predictions
The renewable energy market is expected to grow at an annual rate of 8.4%, reaching $1.5 trillion by 2025. Solar energy leads this growth, anticipated to account for more than 50% of new energy generation capacity. Investment in offshore wind projects is also set to increase dramatically, projected to reach $60 billion by 2030. Policymakers and businesses recognize the economic potential, driving further adoption of renewable solutions. As global awareness of climate change rises, transitioning to clean energy remains a priority, fueling demand in numerous sectors.
Renewable energy technology stands at the forefront of the global shift towards a more sustainable future. Its ability to provide clean power while significantly reducing carbon emissions is vital for addressing climate change. As innovations continue to emerge the potential for efficiency and accessibility grows, making renewable sources more viable than ever.
Investment in these technologies not only supports environmental goals but also stimulates economic growth through job creation and energy independence. Overcoming existing challenges will require collaboration among stakeholders to ensure a robust transition to renewable solutions. With increasing awareness and commitment to clean energy, the future looks promising for renewable energy technology and its role in shaping a healthier planet.