In a world where robots might just take over the kitchen, advanced manufacturing stands as the unsung hero of modern industry. This cutting-edge approach isn’t just about flashy machines and high-tech gadgets; it’s about revolutionizing how products are made. Imagine a factory floor where efficiency meets innovation, and every component is crafted with precision that would make even the most meticulous chef proud.
As industries evolve, advanced manufacturing emerges as the secret sauce for businesses aiming to stay competitive. It’s not just about speed; it’s about smart technology that can adapt and optimize processes on the fly. Whether it’s 3D printing or automation, this is the future of production, and it’s time to get on board or risk being left in the dust—like that old rotary phone collecting dust in the attic. Buckle up as we explore the fascinating world of advanced manufacturing and discover how it’s reshaping our economy.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing encompasses modern production processes that utilize cutting-edge technologies. This approach not only enhances efficiency but also fosters innovation in product design and development. Companies leverage automation, robotics, and data analytics to streamline operations and reduce costs. Adoption of 3D printing facilitates rapid prototyping and customization, significantly enhancing design flexibility. Integration of smart manufacturing systems enables real-time monitoring, creating a more responsive supply chain.
Machine learning plays a crucial role in predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespan. Enhanced data collection and analysis allow manufacturers to optimize workflows and improve quality control. As businesses embrace these technologies, they can tailor solutions to meet specific customer needs. Notably, digital twins provide virtual models of physical processes, allowing for simulation and analysis before actual production begins.
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare have seen substantial benefits from adopting advanced manufacturing techniques. Increased productivity not only results from improved processes but also in better resource management and sustainability efforts. By focusing on innovation and efficiency, companies can gain a competitive edge in the global market.
Challenges do exist, however, including the need for skilled labor and cybersecurity considerations. While advanced manufacturing offers numerous advantages, organizations must address these concerns proactively to fully realize its potential.
Key Technologies in Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing employs various technologies to enhance industry productivity and efficiency. These innovations redefine traditional manufacturing processes.
Automation and Robotics
Automation streamlines repetitive tasks, lowering production times and costs. Robotics plays a vital role in this transformation, handling complex assembly operations with precision. Intelligent machines adapt quickly to changing production demands. Many companies utilize collaborative robots to enhance human labor rather than replace it. The ability to operate with minimal oversight allows for greater operational flexibility. Integrating automation and robotics maximizes output while ensuring consistent quality across products.
Additive Manufacturing
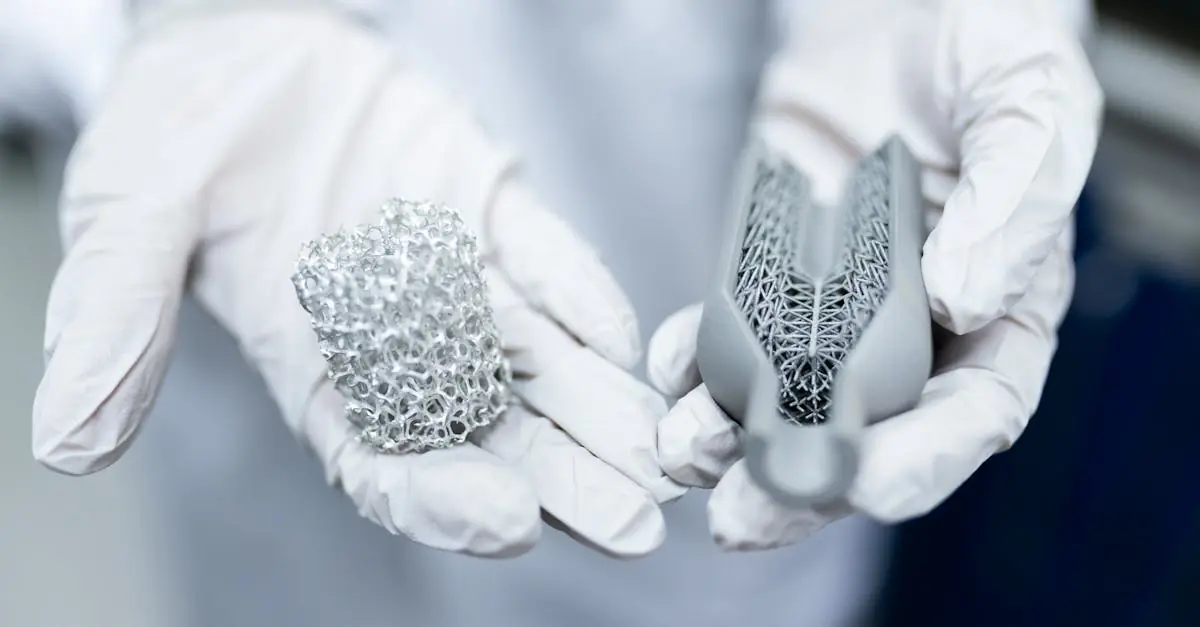
Additive manufacturing, widely known as 3D printing, revolutionizes product design. This technology builds objects layer by layer, reducing material waste significantly. Manufacturers leverage rapid prototyping to test new designs efficiently. Customization becomes more accessible, enabling personalized products that cater to specific consumer needs. Furthermore, industries like aerospace benefit from lighter parts that improve fuel efficiency. By adopting additive manufacturing, companies meet demands for innovation while minimizing production lead times.
Advanced Materials and Composites
Advanced materials and composites enhance product performance in various applications. These materials, such as carbon fiber and graphene, provide superior strength-to-weight ratios. Engineers select these materials for their durability and lightweight properties in aerospace and automotive industries. Innovations in nanotechnology lead to the development of materials with enhanced functionalities. Companies integrate these advanced materials into their products to gain competitive advantages. Improved performance and reduced environmental impact drive the need for ongoing research and development in this area.
Benefits of Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing offers numerous advantages that enhance operational performance across various industries. Companies leveraging these benefits experience significant transformations in their processes.
Increased Efficiency
Automation and smart technology drive remarkable increases in efficiency. Manufacturers achieve streamlined operations through the integration of robotics and real-time data analytics. Predictive maintenance practices further minimize unplanned downtime, allowing for more consistent production schedules. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, accelerating the product development cycle. These collective advancements contribute to faster turnaround times, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market demands.
Cost Reduction
Advanced manufacturing techniques result in substantial cost savings. Utilizing automation and robotics lowers labor costs by replacing repetitive tasks with machines. Enhanced data analytics identifies inefficiencies and reduces waste across production lines. Additionally, 3D printing minimizes material waste by optimizing designs. Businesses can quickly adjust production quantities, reducing excess inventory costs associated with traditional manufacturing processes. Overall, these cost-effective strategies support improved financial performance.
Improved Quality
Quality improvement remains a hallmark of advanced manufacturing. Data-driven quality control systems enhance product consistency by collecting and analyzing performance metrics throughout production. Real-time monitoring allows for immediate corrections, preventing defects before they reach consumers. Employing advanced materials also elevates product performance, ensuring superior durability and functionality. Consistent quality boosts customer satisfaction and reinforces brand loyalty, which are critical factors for long-term success.
Challenges in Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing faces several challenges that can hinder its progress. Skill gaps in the workforce and the complexities of technological integration present significant obstacles.
Workforce Skill Gaps
Skilled labor shortages affect the efficient implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies. Many organizations struggle to find workers proficient in essential areas, such as robotics, data analytics, and automation. Educational institutions often lag behind industry demands, resulting in a talent pipeline that doesn’t meet current needs. Businesses must invest in recruitment and training programs to build a capable workforce. Collaborations with universities can bridge this skill gap and ensure that graduates possess relevant expertise.
Technological Integration
Integrating new technologies into existing manufacturing processes poses challenges for many companies. Legacy systems often lack compatibility with advanced solutions, leading to disruptions in workflow. Companies experience difficulties in adopting data-driven approaches due to inadequate infrastructure. Transitioning to smart manufacturing requires a strategic plan that includes assessing current capabilities and investing in upgrades. Change management strategies assist companies in navigating these shifts effectively, ensuring a smoother integration process.
Future Trends in Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing continues to evolve, driven by technological innovation and a focus on sustainability. Key trends are shaping the future of this sector.
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 revolutionizes manufacturing through the integration of Internet of Things devices. Smart factories use real-time data to optimize production processes. Devices can communicate, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Predictive analytics plays a vital role, providing insights for maintenance needs before failures occur. Automation and robotics enable manufacturers to streamline workflows, allowing for increased flexibility. Implementing smart manufacturing strategies positions businesses to compete effectively in a rapidly changing landscape.
Sustainability Practices
Sustainability practices gain momentum as industries prioritize environmental responsibility. Advanced manufacturing embraces eco-friendly techniques to minimize waste. Companies utilize renewable materials and energy-efficient processes in their operations. Additive manufacturing reduces material use and energy consumption, leading to lower environmental impact. Implementing closed-loop systems fosters recycling and reusing materials, creating a circular economy model. Investment in sustainable practices not only benefits the environment but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Advanced manufacturing is reshaping industries by driving efficiency and fostering innovation. As businesses adopt smart technologies like automation and 3D printing, they position themselves to thrive in a competitive landscape. Embracing these advancements not only enhances operational performance but also addresses the pressing need for sustainability and resource management.
However, companies must navigate challenges such as workforce skill gaps and technological integration. By investing in training and strategic planning, organizations can overcome these hurdles and fully leverage the benefits of advanced manufacturing. The future holds immense potential for those willing to adapt and innovate, ensuring they remain at the forefront of their industries.